No products in the cart.
Return To Shop 0 0
No products in the cart.
Return To Shop Shopping cart (0)
Subtotal: $0.00
Free shipping over 250$
Black Seed Oil for Vitiligo
Could black seed oil be used as a treatment for vitiligo?
Vitiligo is an autoimmune skin that causes white spots due to loss of skin pigment cells (melanocytes). It can affect individuals of all skin colours but is more noticeable in individuals with dark skin.
A randomized, double blind, controlled clinical trial was conducted to compare the effect of Nigella Sativa oil with fish oil on improvement of the vitiligo lesions. This was conducted at a prestigious teaching hospital in Iran. [1]
52 patients were recruited in total and split into each group. Patients applied the oil to lesions twice daily for six months. During the treatment period, skin lesions of patients were evaluated by observers using Vitiligo Area Scoring Index (VASI) tool.
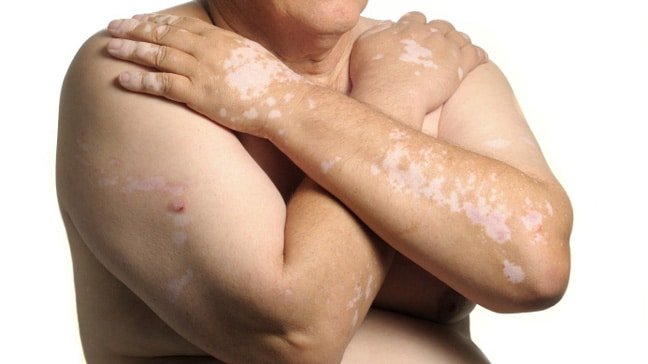
Results
De-pigmented skin areas were reduced over time and the skin colour showed improvement in both groups but much more in the black seed oil group.
After six months, a mean score of VASI decreased from 4.98 to 3.75 in patients applying topical Nigella Sativa and from 4.98 to 4.62 in those using topical fish oil. Most of the percent improvement observed in upper extremities, trunk, head, and neck of those who received Nigella Sativa and head, neck, trunk, and feet of those who received fish oil. No adverse effect was reported by the patients.
The authors hypothesised that one reason for this positive response to treatment is the thymoquinone component of Nigella Sativa. Thymoquinone, the main constituent of Nigella Sativa seeds, protects cells against oxidative damage induced by a variety of free radical-generating pathologies. Thymoquinone can simulate the activity of acetylcholine, which causes the release of melanin and darkening of the skin through stimulation of cholinergic receptors.
